





Frequently Asked Questions about the Ancient Olympic Games
- Where did the Olympic games come from?
- Why were they held at Olympia?
- Were there other contests like the Olympics?
- Who could compete in the Olympics?
- Were women allowed at the Olympics?
- How were the athletes trained?
- What prizes did Olympic victors get?
- Who were the Olympic judges?
- What was the penalty for cheating?
- Where did the marathon come from?
- When did the ancient games begin and when did they end?
Where did the marathon come from?
The marathon was never one of the ancient Olympic events, although its origin dates back to another episode in ancient Greek history.
In the 5th century B.C., the Persians invaded Greece, landing at Marathon, a small town about 26 miles from the city of Athens. The Athenian army was seriously outnumbered by the Persian army, so the Athenians sent messengers to cities all over Greece asking for help.
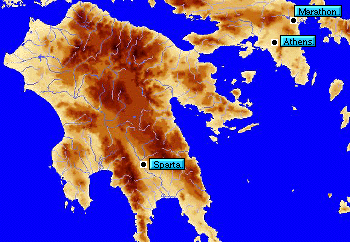
The traditional origin of the marathon comes from the story how a herald named Phidippides ran the 26 miles from Marathon to Athens to announce the Greek victory and died on the spot. Phidippides was sent by the Athenians to Sparta to ask for help; a man named Eukles announced the victory to the Athenians and then died. Later sources confused the story of Phidippides, also called "Philippides," with that of Eukles. Although most ancient authors do not support this legend, the story has persisted and is the basis for the modern-day marathon.

Main panel: runner on right
Photograph by Maria Daniels, courtesy of The University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology
The modern Olympic marathon is approximately 26 miles and usually takes over 2 hours for athletes to finish.
To read more about these topics, see Further Resources.
This exhibit is a subset of materials from the Perseus Project database and is copyrighted. Please send us your comments.